
Continuous Improvement Software
Thriving Through Improvement
Yambla Continuous Improvement Software helps companies foster a culture of continuous improvement and empowers teams to streamline the process of identifying, evaluating, and implementing improvements across various aspects of their operations.
- ✔ Try for free
- ✔ No credit card required
- ✔ Cancel anytime
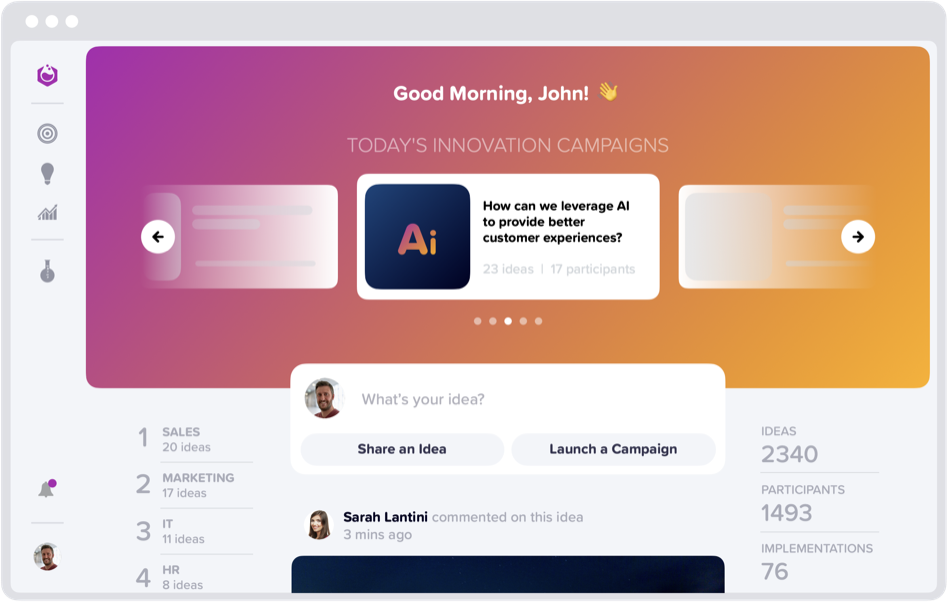
Yambla provides a centralized platform for capturing, evaluating, and implementing improvement ideas from employees at all levels of the organization. With Yambla, companies can crowdsource ideas for process optimization, product enhancements, cost reduction, and more, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. Yambla facilitates iterative feedback loops that enable teams to solicit input, gather insights, and iterate on their ideas and initiatives. By encouraging open communication and collaboration, Yambla empowers teams to refine their strategies and approaches continuously, driving incremental improvements over time.
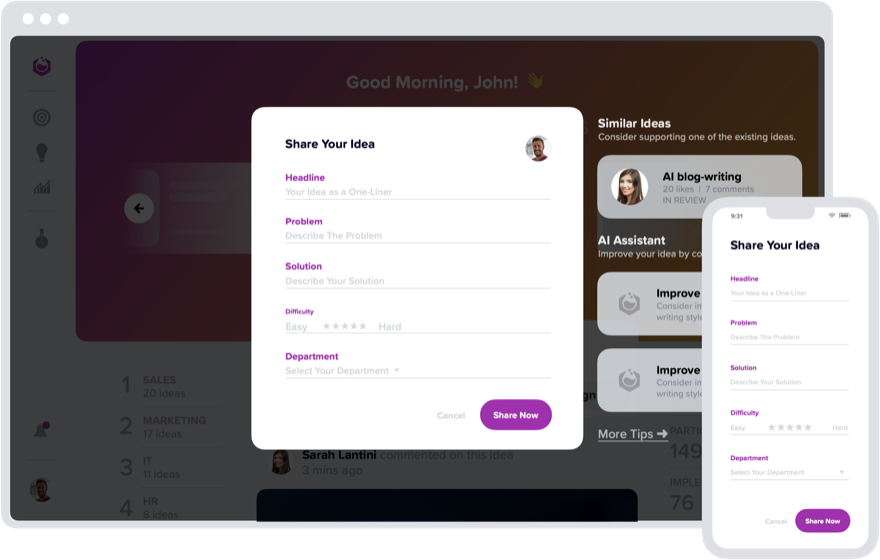
Capture Ideas
Enable your employees, partners and customers to submit their ideas anytime, anywhere. Whether it's a stroke of genius or a fleeting thought, capturing it is just a click away. Choose from a variety of idea formats, from text descriptions to multimedia attachments, sketches and video pitches.
Discover More Features →
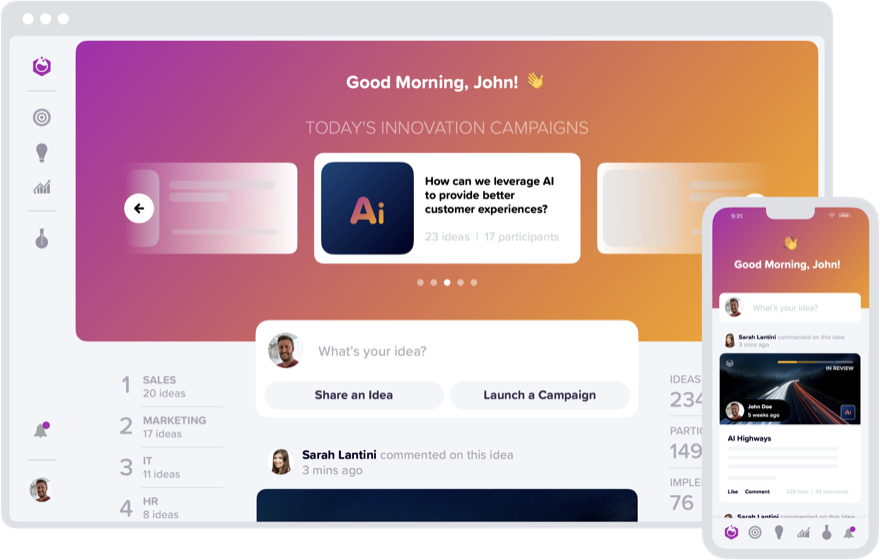
Social Media Interface
Yambla's interface is designed to be intuitive and easy to navigate, similar to the social media platforms that users are already familiar with. This familiarity lowers the barrier to entry, making it effortless for employees to engage with the platform and contribute their ideas and insights. Yambla facilitates communication among team members through features such as comments, likes, and mentions, mirroring the interactive nature of social media.
Discover More Features →
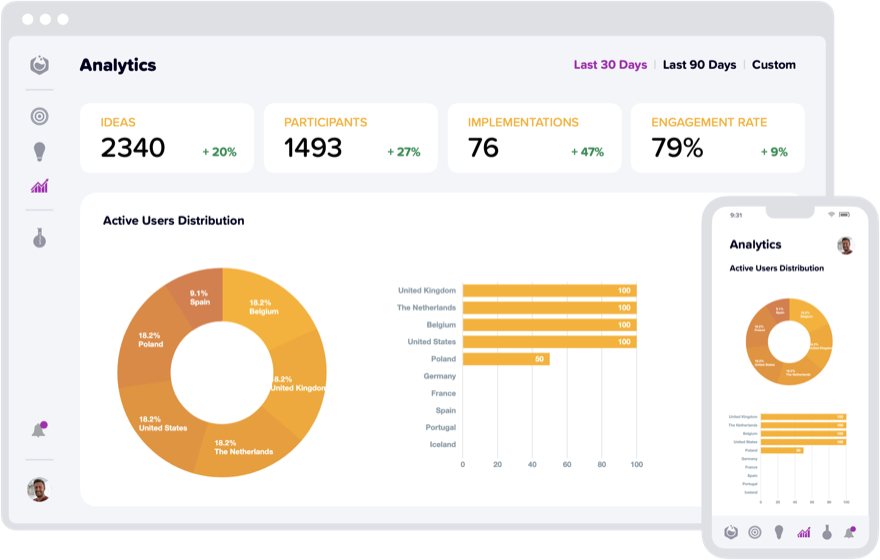
Measure Engagement
Gain deep insights into user behavior with our comprehensive suite of metrics. From user interactions to session durations, we provide a holistic view of engagement across various touchpoints. Drill down into your data with advanced segmentation capabilities. Identify key user segments, track their engagement levels, and tailor your strategies to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Discover More Features →
Other Highlighted Features
Idea Forms
Customize your own forms.
Full Media Support
Attach any media.
Duplicate Detection
Detect duplicate ideas.
Community Voting
Set up idea voting.
Prioritization
Prioritize ideas quickly.
Dormant Idea Detection
Identify dormant ideas.
Discover More Features →
Distinctly Us
Experience an exceptional product with even more exceptional customer service.
Continuous Improvement Is Just The Beginning
Fuel innovation with one flexible solution, allowing you to launch any program format effortlessly.
Discover Our Product Suite →
What is Continuous Improvement?
Continuous improvement, also known as continuous improvement process (CIP) or continuous improvement management (CIM), is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and implementing incremental changes to processes, products, services, or operations in order to enhance efficiency, quality, and overall performance. The goal of continuous improvement is to achieve ongoing, incremental enhancements that collectively lead to significant improvements over time.
Key characteristics of continuous improvement include:
- Iterative Approach: Continuous improvement is not a one-time effort but rather an ongoing cycle of analysis, implementation, and evaluation. The process is repeated regularly to ensure that improvements are sustained and refined.
- Problem Identification: It begins with identifying areas that need improvement. This could involve analyzing processes, gathering feedback from stakeholders, monitoring performance metrics, and looking for bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Data-Driven: Continuous improvement relies on data and evidence to guide decision-making. Quantitative and qualitative data are used to identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern.
- Small, Incremental Changes: Instead of large-scale overhauls, continuous improvement focuses on making small, manageable changes. These changes are less disruptive and easier to implement, reducing the risk of negative impacts.
- Feedback and Collaboration: Employees and stakeholders at all levels are encouraged to provide input and suggestions for improvement. Collaboration fosters a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
- Experimentation: Trying out new approaches and solutions is a key aspect of continuous improvement. This encourages experimentation with different ideas to see what works best.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Once changes are implemented, their effects are closely monitored to ensure they are producing the desired results. If needed, further adjustments can be made.
- Documentation: The continuous improvement process should be documented to track changes, outcomes, and lessons learned. This documentation becomes a valuable resource for future reference.
- Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach: While leadership often drives the continuous improvement initiative, input from employees who directly interact with processes is also crucial. Both top-down and bottom-up perspectives contribute to comprehensive improvements.
- Cultural Emphasis: Successful continuous improvement requires a supportive organizational culture that values learning, adaptation, and the pursuit of excellence.
Continuous improvement methodologies and frameworks include Lean, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), Kaizen, and Agile. These approaches provide structured techniques and tools for implementing and managing continuous improvement initiatives effectively.
Continuous improvement is not limited to any specific industry or sector. It is applicable to manufacturing, services, healthcare, education, technology, and more. By constantly striving to identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and optimize processes, organizations can maintain a competitive edge and better meet the changing needs of their stakeholders.
Powering Collaborative Innovation worldwide.
Get Started Today!
Trusted by some of the world’s smartest companies









